Objective: Find all lines in a file that only contain alpha characters and delete or replace.
Sample contents of file.
Z2j2NH23
VTQnPwSS
hFbxgvFt
VSVR8v3F
GPrP4zo
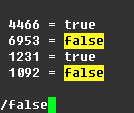
The following sed command works for our objective.
sed s/[[:alpha:]]\{8\}/ALPHAONLY/g file.txt
The part in the [] tells sed to search for any alpha characters a-Z, the part in bold \{8\} tells it to search 8 spaces out (Change if needed) and ALPHAONLY is what alpha line will get substituted to.
sed s/[[:alpha:]]\{8\}/ALPHAONLY/g
Returns
Z2j2NH23
ALPHAONLY
ALPHAONLY
VSVR8v3F
GPrP4zo9
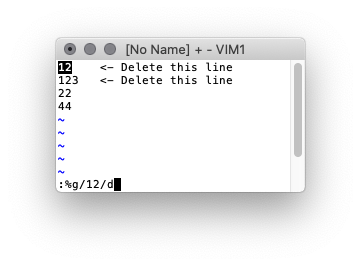
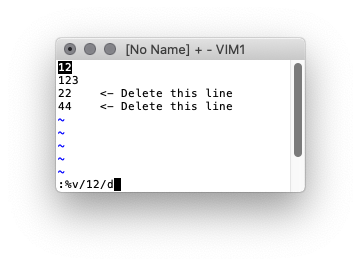
You can run the same basic syntax in VI
Search and replace
:%s/[[:alpha:]]\{8\}/ALPHAONLY/g
Or to delete the lines
:%d/[[:alpha:]]\{8\}/d
You can also change [[:alpha:]] for [[:digit:]] if you want to search for numbers instead.