Looks like you can use Darling to run MacOS command line applications in Linux.
Tag Archives: linux
Firefox performance improvements for Linux
Bunch of tweaks and enhancements are on the arch wiki
https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Firefox/Tweaks
Two specific ones that can help with performance are enabling OMTC and WebRender
https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Firefox/Tweaks#Enable_OpenGL_Off-Main-Thread_Compositing_(OMTC)
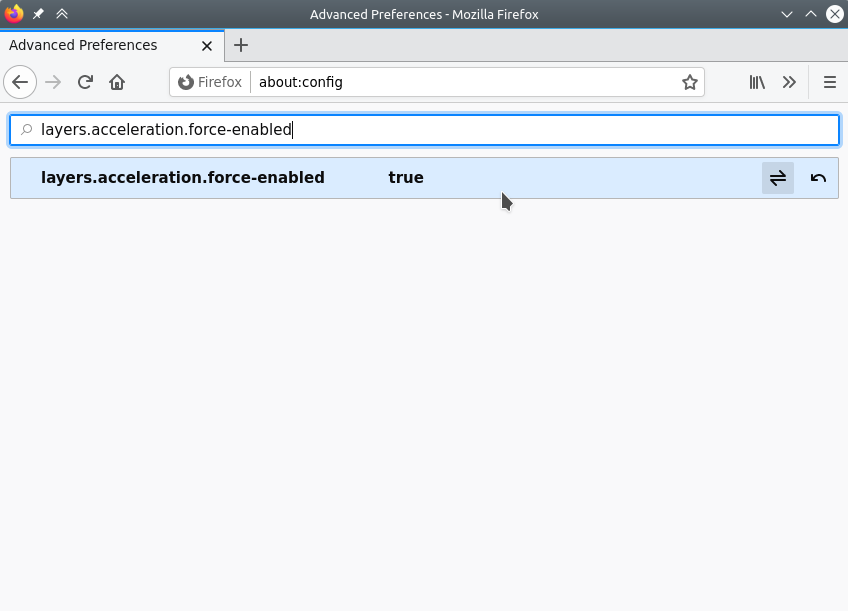
Open up Firefox and about:config
Search for “layers.acceleration.force-enabled”
Search for “gfx.webrender.all” and set to true
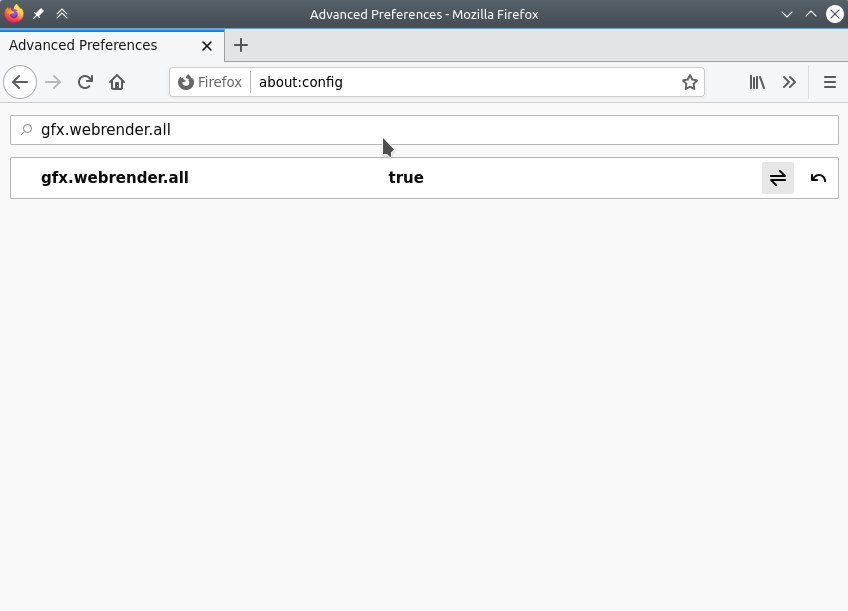
Restart Firefox.
Reset NextCloud admin password – Snap package
The regular command to reset the password for a NextCloud user does not work when NextCloud is installed from a snap package.
$ sudo -u www-data php /var/www/nextcloud/occ user:resetpassword admin Could not open input file: /var/www/nextcloud/occ
The reason is that NextCloud is located in “/snap/nextcloud”
Unfortunately the occ file is not located in /snap/nextcloud/current/
However, you can run the nextcloud.occ command directly without specifying the path. Change admin to your user.
sudo nextcloud.occ user:resetpassword admin
Type in the new password twice and login.
Alienware fan control in Linux notes
Helpful links
https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Fan_Speed_Control#Dell_laptops
https://bbs.archlinux.org/viewtopic.php?id=248106
https://www.reddit.com/r/Dell/comments/9pdgid/configuring_the_xps_to_play_nice_with_linux
You can use the following commands to “initilize” the fans so the fancontrol can read them.
sudo modprobe dell-smm-hwmon ignore_dmi=1sudo sensors-detect
After that is done you should be able to setup a fancontrol config with
sudo pwmconfig
After it is set up you can launch fancontrol to control the fans
sudo fancontrol
If you want to tweak the setting, modify the fancontrol config under
/etc/fancontrol
or run pwmconfig again and replace config.
Sounds like you should be able to add the following to “etc/modprobe.d/dell.conf” to get it to run on boot.
options dell-smm-hwmon ignore_dmi=1
Install AppImage Application
https://askubuntu.com/questions/774490/what-is-an-appimage-how-do-i-install-it
It appears that all you have to do is
chmod +x application.AppImage
and then you can run the image directly
./application.AppImage
Example:
bob@localhost:~$ chmod +x Downloads/Vysor_2.2.1.AppImage bob@localhost:~$ Downloads/Vysor_2.2.1.AppImage
Install snap on Linux Mint
Info from here https://snapcraft.io/docs/installing-snap-on-linux-mint
Install snapd with
sudo apt install snapd -y
You should now be able to install snap packages
sudo snap install package.snap
Install GDM as default display manager
Install Gnome Display Manager if it is not already installed
sudo apt install gdm3
Stop and disable the currently display manager, replace sddm with the current display manager. May be lightdm
sudo systemctl disable sddm
sudo systemctl stop sddm
Enable GDM
sudo dpkg-reconfigure gdm3
sudo systemctl enable gdm3
sudo systemctl start gdm3
Should be good to go.
Unlock Linux Lock Screen
List current sessions with
loginctl list-sessionsUnlock with session number from above command.
loginctl unlock-session session-numberOr to unlock all sessions do
loginctl list-sessionsMore info:
https://askubuntu.com/questions/341014/unlock-login-screen-using-command-line
Linux Command to make computer go to Sleep
You can tell the computer to go to sleep by executing the following command from a terminal
systemctl suspend
The computer should immediately go to sleep.
Sleep with delay
If you would like to add a delay you can do the following. Replace 5 with the number of seconds you want to wait.
sleep 5 && systemctl suspend
Linux, Send USR1 signal to pid
In Linux you can send signals to a process id to trigger actions for the program. Useful scenario for this is to renew an IP address on a device that uses udhcpc. You should be able to change udhcpc for other programs, you’ll just need to read the help for that specific program.
In the udhcpc help it says
Signals:
USR1 Renew lease
USR2 Release lease
But how do we send those signals to udhcpc? Answer, use the kill command.
kill: kill [-s sigspec | -n signum | -sigspec] pid | jobspec … or kill -l [sigspec]
Send a signal to a job.
Send the processes identified by PID or JOBSPEC the signal named by SIGSPEC or SIGNUM. If neither SIGSPEC nor SIGNUM is present, then SIGTERM is assumed.
Options:
-s sig SIG is a signal name
-n sig SIG is a signal number
-l list the signal names; if arguments follow `-l' they are
assumed to be signal numbers for which names should be listed
-L synonym for -l
Kill is a shell builtin for two reasons: it allows job IDs to be used instead of process IDs, and allows processes to be killed if the limit on processes that you can create is reached.
Exit Status:
Returns success unless an invalid option is given or an error occurs.
We see from above that we can pass a signal name in using the -s option.
So to send USR1 signal to udhcp we do the following
kill -s USR1 pid_of_udhcpc
Replace pid_of_udhcpc with the actual pid or use the following command to find the pid
kill -s USR1 $(pgrep udhcpc)
“pgrep udhcpc” prints the pid of the searched for process.
Helpful links
https://www.thegeekstuff.com/2011/02/send-signal-to-process/
https://www.linux.org/threads/kill-signals-and-commands-revised.11625/
