We are going to setup a Samba/CIFS share on Fedora Server that we will then access from Windows 10.
- Install Samba/CIFS server packages
- Create user to access share
- Configure SELinux and firewall
- Connect to erver from Windows
1. Install Samba/CIFS Fedora Server Packages
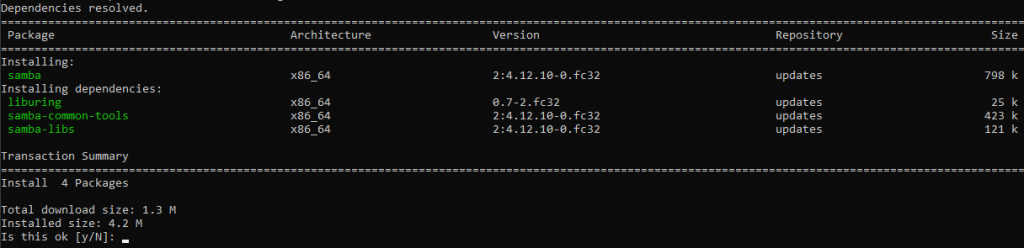
First we need to install the samba package.
sudo dnf install samba
Next, lets enable the Samba service so it automatically starts when the server boots up.
systemctl enable smb nmb systemctl start smb
nmb is a “NetBIOS name server that provides NetBIOS over IP naming service to clients”
https://www.samba.org/samba/docs/current/man-html/nmbd.8.html
2. Setup Samba/CIFS User
We now need a user to connect to the Samba share with. You can use the commands below to to create a new user.
pdbedit only configures a current Linux system user for Samba. You can skip creating a new Linux user, but only if there is one already created that you can use.
sudo useradd -m sambaUser sudo passwd sambaUser sudo pdbedit -a sambaUser
3. Configure Server SELinux and Firewall Permissions
Configure SELinux permissions with the following command.
sudo setsebool -P samba_enable_home_dirs on
You can also just disable SELinux. Although it is not necessarily recommended.
How To Enable/Disable SELinux
sudo setsebool -P samba_enable_home_dirs on sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=samba --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --reload
4. Test Samba/CIFS Share from Windows
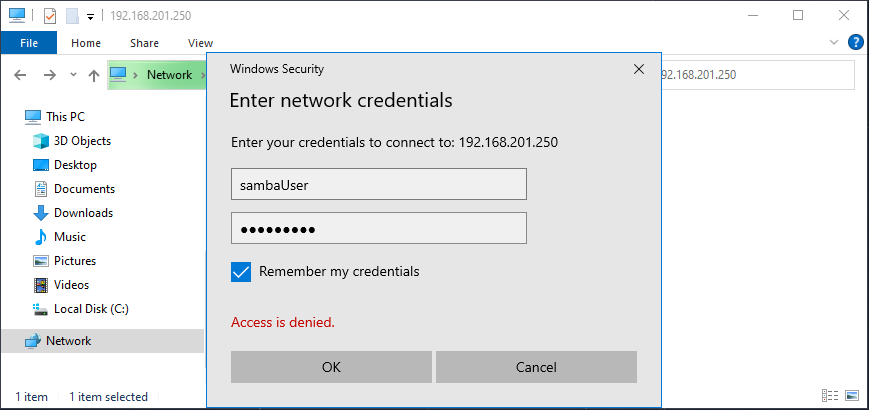
You can now test to see if the share works. Open up Windows Explorer. Type in the IP address of the server and connect.
\\ip-address\sambaUser
It should prompt you for a login. Enter the user and password you set up.
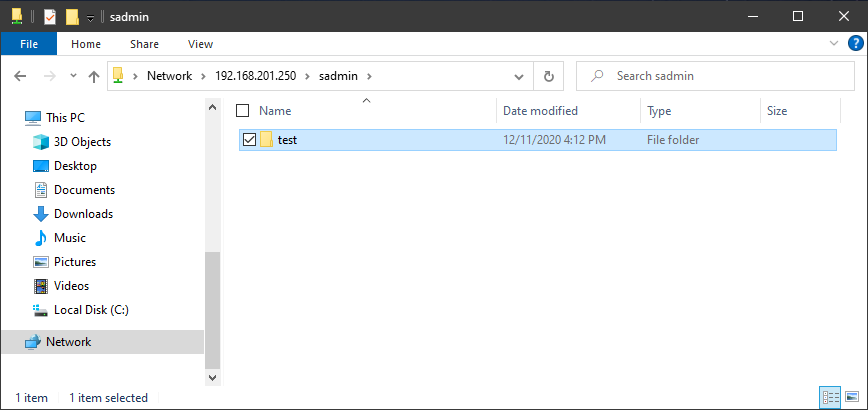
If it loads, then congratulations! You have successfully setup a Samba/CIFS Share on Fedora Server. Create new directories or files or whatever else you need.
Check out the following links for more information about setting up Samba.
https://fedoramagazine.org/fedora-32-simple-local-file-sharing-with-samba/
https://jewelhuq.wordpress.com/2017/12/08/how-to-install-samba-server-in-fedora/
https://fedoramagazine.org/fedora-32-simple-local-file-sharing-with-samba/
