There are a couple different options for undeleting files for XFS filesystems.
TestDisk
TestDisk is a great command line recovery tool. Unfortunately, it can be slightly more difficult on systems using XFS compared to EXT4 systems. TestDisk does not support undeleting a file in place on XFS.
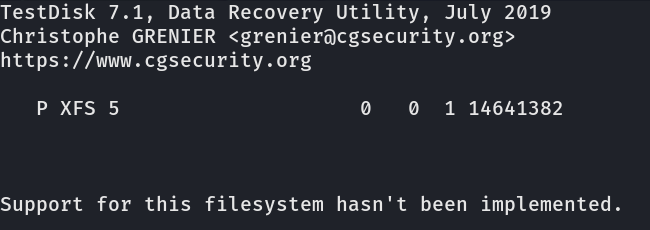
You can still recover files using TestDisk, you just need to recover the whole drive and dig through the recovery results to find the files you want.
xfs_undelete
There is also another utility that can be helpful. xfs_undelete
https://github.com/ianka/xfs_undelete
It allows for a little more flexibility in recovering files. For instance, you can specify to recover the files from the past hour to recover.
Download prerequisites
sudo dnf install tcllib wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ianka/xfs_undelete/master/xfs_undelete chmod u+x ./xfs_undelete ./xfs_undelete
Example of running xfs_undelete
./xfs_undelete -t -1hour ./dev/sda2
You will need a different filesystem to save the files to. Otherwise you will receive the following error.
Your output directory is /home/bob/recovery/ That is within the filesystem / you want to recover files from. This isn't feasible as it would overwrite the deleted files you wanted to recover. Please specify the option -o /path/to/output_directory on another (rw mounted) filesystem or run xfs_undelete from within a directory on that filesystem so the recovered files could be written there. They cannot be recovered in place.
It’s not the greatest idea to recover on the system while running. Ideally, shut the system down, plug the drive into another machine as read only, and copy the files off.
You could also boot up in single user mode or a live Linux iso/thumbdrive and mount another recovery drive. Should work for both physical and virtual environments.