Notes on installing OpenVAS on Kali Linux in 2023/2024
sudo apt install openvas
Run the setup script. This used to be called openvas-setup, now it is gvm-setup. Note that the script can take a long time to run.
gvm-setup
At the end of the script, it will give you a password. Use this password to log into the web interface. You can reset the password if needed.
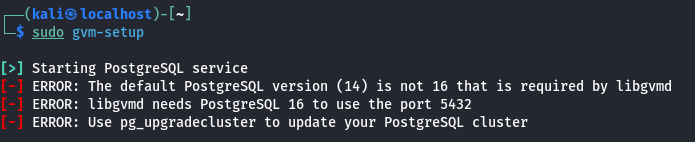
If you run into issues with PostgreSQL, check out this post
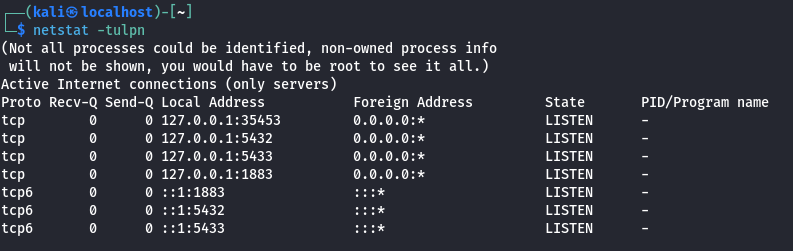
Log into the web interface at
https://127.0.0.1:9392
Troubleshooting
On Kali Linux, you need to run commands as the _gvm user. You can do this by prepending the commands with
sudo runuser -u _gvm -- COMMAND
There are two — dashes, between the _gvm user and the COMMAND. Replace COMMAND with the GVM/OpenVAS command you want to execute.
Example, to list the current users do
sudo runuser -u _gvm -- gvmd --get-users
To create a new user run
sudo runuser -u _gvm -- gvmd --user=newadmin --new-password=longsecurepassword
Failed to find config ‘daba56c8-73ec-11df-a475-002264764cea’
If you receive a `Failed to find config ‘daba56c8-73ec-11df-a475-002264764cea'”` error,
try running the following command
sudo runuser -u _gvm -- greenbone-nvt-sync
This can take awhile, but it should sync all the files needed. Check the following link for more information.
https://forum.greenbone.net/t/cant-create-a-scan-config-failed-to-find-config/5509
The following link is also helpful for installing OpenVAS
https://stafwag.github.io/blog/blog/2021/02/28/howto-install-opevas-on-kali/