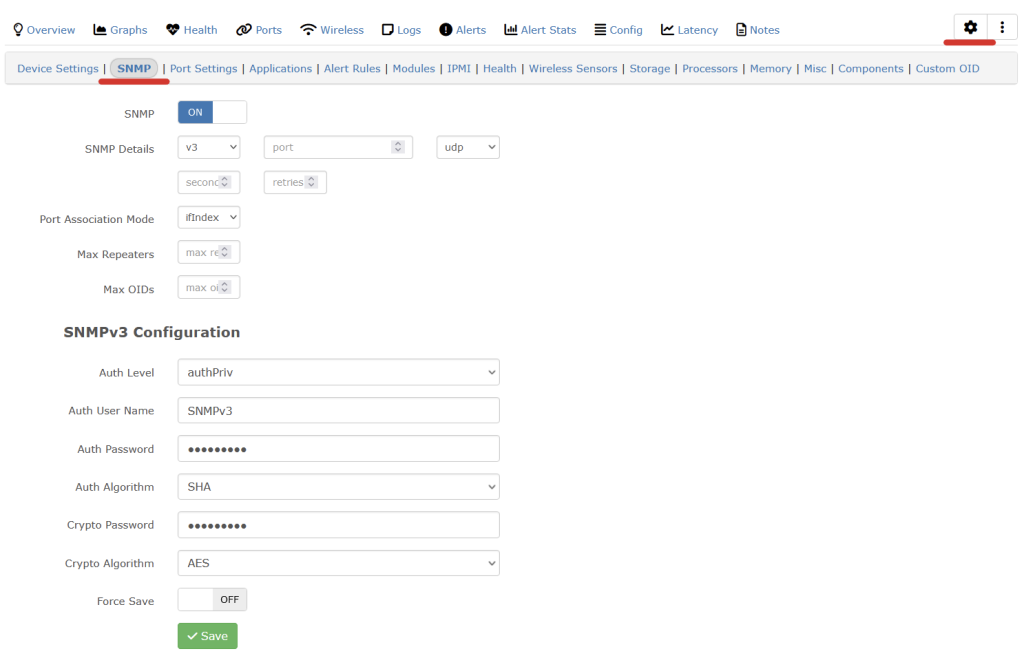
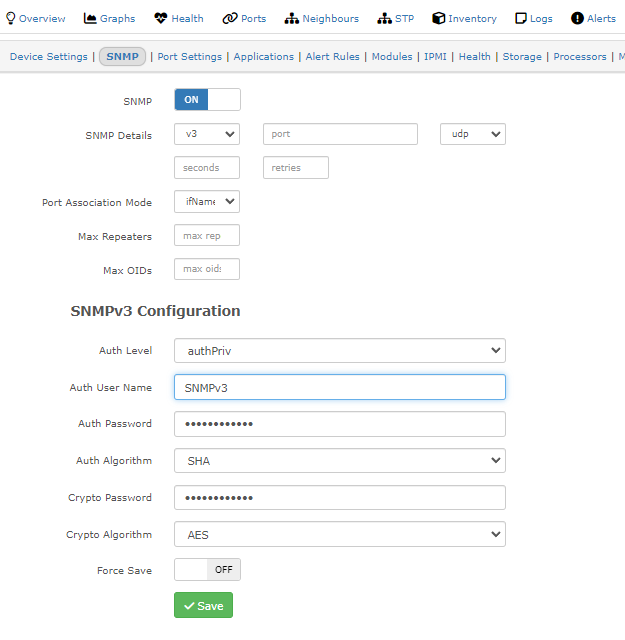
LibreNMS uses fping to check if devices are up or not. So if something is broken with fping, say a SELinux permission, you can receive the “Could not ping” error, while trying to add a new device.
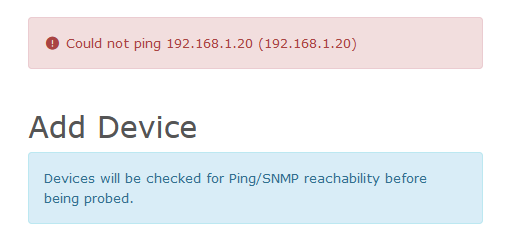
First we need to verify that fping is working. SSH into the LibreNMS server and try pinging an address.
fping 192.168.1.20
There was an issue with fping working if ipv6 was disabled. If fping is not working at all, check out this thread.
If you get an alive or unreachable message, then we know fping is working and can move on to the next stage of troubleshooting.
If you are using SELinux, then there is a good chance the problems has to do with that. You can try rerunning all the SELinux commands from the install guide. Note that it has a specific portion for fping.
https://docs.librenms.org/Installation/Install-LibreNMS/#selinux
If it is still not working, we can take a look at the issue with the audit2why command and feed in the audit log.
audit2why < /var/log/audit/audit.log
Here is some example output.
[root@librenms ~]#
type=AVC msg=audit(1676192040.183:404404): avc: denied { bind } for pid=128555 comm="fping" lport=1 scontext=system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 tcontext=system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 tclass=rawip_socket permissive=0
Was caused by:
Missing type enforcement (TE) allow rule.
[root@librenms ~]#
Another, perhaps more effective way to check the log is to follow it using the “tail -f” command.
tail -f /var/log/audit/audit.log | grep denied
And then in the web browser, try adding a new device. If SELinux is blocking it, it should throw a denied entry.
Example output
type=AVC msg=audit(1676192040.183:404404): avc: denied { bind } for pid=128555 comm="fping" lport=1 scontext=system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 tcontext=system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 tclass=rawip_socket permissive=0
Now we have verified that the issue is SELinux permissions related. We can create a module to allow it.
audit2allow -a -M fping_http < /var/log/audit/audit.log
And apply the module with
semodule -i fping_http.pp
You may need to do this a couple times. Check the audit log again to see if anything new shows up. Notice the slight difference in this error compared to the above error.
# tail -f /var/log/audit/audit.log | grep denied
type=AVC msg=audit(1676192613.121:404409): avc: denied { node_bind } for pid=153257 comm="fping" scontext=system_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 tcontext=system_u:object_r:node_t:s0 tclass=rawip_socket permissive=0
We’ll create a new module for this and apply it
audit2allow -a -M node_http < /var/log/audit/audit.log semodule -i node_http.pp
Not sure that is the best way to fix the problem. But it appears that SELinux is keeping Apache “httpd” from running fping which is why we need to create and load the modules.