Note:
- This is not a comprehensive guide, if you need more info, refer to the installation manual here.
- This assumes that all your partitions are going to be on one drive
Installing CentOS 7
Note: If you have issues installing CentOS via the default install interface, try using the Fallback graphics mode, found in the Grub boot menu under “trubbleshooting”.
Install CentOS like you normally would, just be sure to leave at least 60GB of free space for Docker/Zenoss
You can Select Automatic Partitioning, but you will need to make additional space available. I just configured it manually.
Note that I have about 75GB of free space, this will be used for “/var/lib/docker” and “/opt/serviced/var/volumes”. We’ll set these up later on.
You don’t necessarily need to setup a user, but you can if you want to.
Configuring CentOS for Zenoss
Setup network
You will need to setup your network settings. Refer to this post to set a static IP address if needed.
Note: In CentOS 7 ifconfig is not installed by default. If you need to check the IP address use the following command.
ip addr shAfter your connected to the internet you can install ifconfig with
yum install -y net-toolsSetup Hostname
Zenoss seems to have issues if you change the hostname after it is installed so be sure to set up the hostname before you start installing zenoss.
Check current hostname
hostnameChange the hostname. Replace “newhostname” with your new hostname.
hostnamectl set-hostname newhostnameAfter you finish configuring the hostname, add it to “/etc/hosts” with the following command. Change the IP address and the hostname “zenoss” to your systems IP address and hostname.
echo "192.168.56.101 zenoss" >> /etc/hostsUpdate your system
yum update -yDisable Firewall
systemctl stop firewalld && systemctl disable firewalldEnable persistent log storage
mkdir -p /var/log/journal && systemctl restart systemd-journaldCreate two Btrfs file systems
First create two normal linux partitions using your favorite disk utility. I am using cfdisk. Each partition should be over 30GB.
cfdisk /dev/sdaCreate two Primary partitions and put them at the end and then write and exit.
Take note of the two new partitions names. Mine are “sda4” and “sda3”.
After the above changes are made, it would be a good idea to reboot the machine so the partition table can be updated.
rebootNow we will reformat the two partitions as Btrfs
Create mount point.
mkdir -p /var/lib/docker /opt/serviced/var/volumesChange “/dev/sda3” and “/dev/sda4” to your partitions names if they are different.
DOCKER_PART=/dev/sda3 APP_PART=/dev/sda4 mkfs -t btrfs --nodiscard $DOCKER_PART mkfs -t btrfs --nodiscard $APP_PARTAdd the new file systems to fstab, so they automatically mount on boot.
APP_PATH="/opt/serviced/var/volumes" echo "$DOCKER_PART /var/lib/docker btrfs rw,noatime,nodatacow 0 0" >> /etc/fstab echo "$APP_PART $APP_PATH btrfs rw,noatime,nodatacow 0 0" >> /etc/fstabMount the new filesystems, and make sure that they mounted
mount -a if [[ `mount | egrep 'docker|serviced'` ]]; then echo "Mounted" ; else echo "Not Mounted" ; fiYou can manually check by running the following command.
mount | egrep 'docker|serviced'you should receive something like the following
/dev/sda3 on /var/lib/docker type btrfs (rw,noatime,seclabel,nodatasum,nodatacow,space_cache) /dev/sda4 on /opt/serviced/var/volumes type btrfs (rw,noatime,seclabel,nodatasum,nodatacow,space_cache)Disable SELinux
By default SELinux is installed and enabled. To disable SELinux either edit the config file “/etc/selinux/config” and change “SELINUX=enforcing” to “SELINUX=disabled”, or you can run the following command.
EXT=$(date +"%j-%H%M%S") sudo sed -i.${EXT} -e 's/^SELINUX=.*/SELINUX=disabled/g' \ /etc/selinux/config && \ grep '^SELINUX=' /etc/selinux/configEnable Dnsmasq
systemctl enable dnsmasq && systemctl start dnsmasqInstall and Configure NTP
yum install -y ntp && systemctl enable ntpdHave NTP start on system boot and then start NTP
echo "systemctl start ntpd" >> /etc/rc.d/rc.local chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local systemctl start ntpdDownload and install the Zenoss repository
rpm -ivh http://get.zenoss.io/yum/zenoss-repo-1-1.x86_64.rpm yum clean allFinal Reboot
reboot
Installing Zenoss
Once your logged back into the system start installing zenoss
Install the Zenoss-core service and start docker
yum --enablerepo=zenoss-stable install -y zenoss-core-service systemctl start docker
Add the Btrfs and DNS flags to the Docker startup options
Identify ip for docker
ip addr | grep -A 2 'docker0:' | grep inet
Add the docker startup options. Change the ip address if needed. It should match the one from the previous command.
echo 'DOCKER_OPTS="-s btrfs --dns=172.17.42.1"' >> /etc/sysconfig/docker
Change the volume type for application data
You can manually edit the serviced file “/etc/default/serviced” and change the variable “SERVICED_FS_TYPE” from “rsync” to “btrfs” or run the following command.
EXT=$(date +"%j-%H%M%S")
sudo sed -i.${EXT} \
-e 's|^#[^S]*\(SERVICED_FS_TYPE=\).*$|\1btrfs|' \
/etc/default/serviced
Restart docker
systemctl stop docker && systemctl start docker
Start the control center
systemctl start serviced
you can monitor the process with
journalctl -u serviced -f
Serviced has about 5-10 minutes worth of work to do before you’ll be able to login to the Control Center interface. If the service fails to start, reboot the server.
Setting up name resolution
To setup name resolution on you local computer just add the following line to your “hosts” file. On Linux and OS X this is located in “/etc/hosts” On Windows machines it is under “\Windows\Sytem32\Drivers\etc\hosts”
192.168.56.101 hostname zenoss5.hostname hbase.hostname opentsdb.hostname rabbitmq.hostname
Be sure to change the IP address and “hostname” to the IP address and hostname of your server. You also might need administrative privileges to edit the hosts file.
Logging into the Control Center.
Now open up a web browser and go the following URL. Change the IP address to your servers IP.
https://192.168.56.101
Login with the Zenoss server root username and password. If you want to setup a user other then root, please refer to the Zenoss Installation guide here.
Change the hostname to your Zenoss server hostname
Select the check boxes in the next two steps.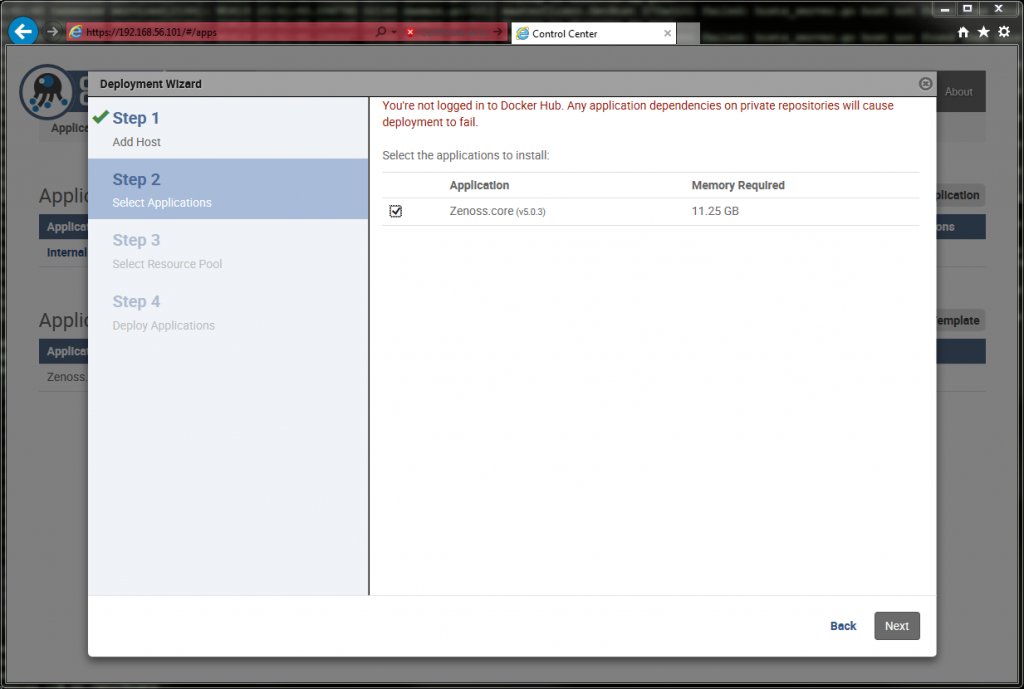

Give it a deployment id and deploy it.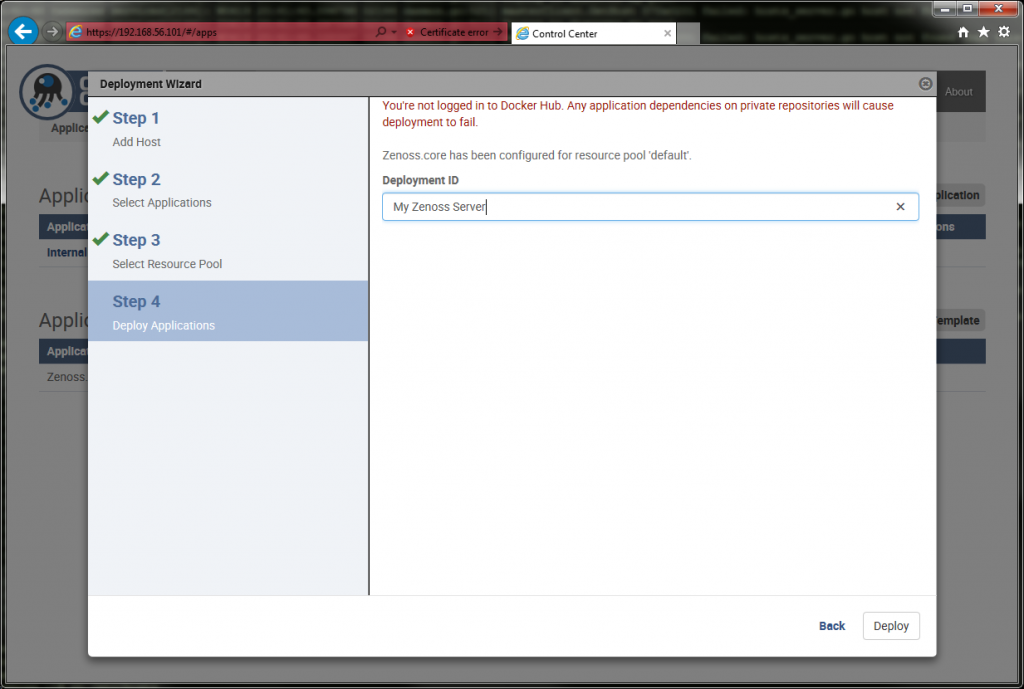

Once it is deployed Make sure that it is started. Once it finishes go log into Zenoss. It can take awhile for Zenoss to start up, depending on your hardware, so be patient.
The Direct URL for Zenoss is
https://zenoss5.hostname









