Here is a list of helpful Postgres commands
Drop a Role
DROP ROLE role_name;
Connect to database
\c database_name;
List tables
\l
List tables in current database
\dt
List users
\du
A better Cheat Sheet

Here is a list of helpful Postgres commands
Drop a Role
DROP ROLE role_name;
Connect to database
\c database_name;
List tables
\l
List tables in current database
\dt
List users
\du
A better Cheat Sheet
We’ll be using telnet to connect to a mail server and send ourselves an email.
The parts in bold are the commands to enter.
[bob@linux ~]$ telnet mail.website.com 25 Trying mail.website.com... Connected to mail.website.com. Escape character is '^]'. 220-mail.website.com ESMTP Exim 4.85 #2 Mon, 09 May 2022 22:12:59 220-We do not authorize the use of this system to transport unsolicited, 220 and/or bulk e-mail. HELO domainto.sendfrom.com 250 mail.website.com Hello domainto.sendfrom.com [192.168.1.2] MAIL FROM: <bob@incredigeek.com> 250 OK RCPT TO: <bob@incredigeek.com> 250 Accepted DATA 354 Enter message, ending with "." on a line by itself Subject: Test Message This is a test . 250 OK id=5a1g7i-1347MT-1p QUIT 221 mail.website.com closing connection Connection closed by foreign host.
Further links to read
https://github.com/maildev/maildev/issues/212
Bob has a computer running Fedora. When he installed Fedora he didn’t setup the root password and locked the root account. That is best practice. Right? Then one day he goes to upgrade to the latest version of Fedora and types in
sudo dnf update
and is greeted with
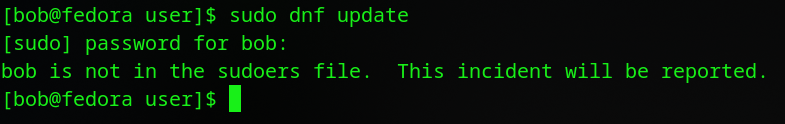
What happened? I had access before? Bob thinks to himself. Seems like I am not in the wheel group anymore. Bob being a smart person decides to attempt recovery mode. He’ll boot up and just readd his user to the wheel group.
Recovery mode starts up and then fails due to the root account being locked. What?!
Bob then starts talking to himself as he is in need of some expert advice. What other options do I have. I know! He runs to find his handy dandy Live Fedora pen drive. Plugs it in and boots up into a live version of Fedora. Now I can mount and access the main drive.
But wait, I can’t run “usermod -G wheel bob” because that will only affect the Live System. I could chroot into the drive. That would require mounting some extra mount points. Is there a faster way? We could maybe edit the /etc/group and add “wheel:x:10:bob”. That should add bob back to the wheel group. Right?
Wait, what about the sudoers file. We are normally supposed to use “sudo visudo” command to modify the file. Let’s check the file and see if we can just manually edit it.
$ stat -c "%n %a" /etc/sudoers /etc/sudoers 440 $
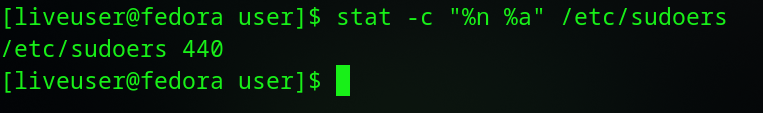
Hmm, okay I am going to need to change permissions to save the file. Let’s chmod that to 644 temporarily
$ sudo chmod 644 /etc/sudoers
Alright now I should be able to edit it.
$ sudo vi /etc/sudoers
Okay, now I need to explicitly give myself permission to use sudo. Where is that line. Ah-ha!
root ALL=(ALL) ALL
Lets duplicate that with yy and p, replace root with my username.
root ALL=(ALL) ALL bob ALL=(ALL) ALL
Save that with esc then :wq enter
Now change the file permissions back
sudo chmod 400 /etc/sudoers
Reboot the system and now lets login and test sudo.
$ sudo whoami root
Success!
Bob, satisfied that the problem is resolved, rewards himself by getting a sandwich.
sudo make me a sandwich
https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/quick-docs/root-account-locked/
Adding a directory to your path is really easy.
The following command adds the ~/script_folder to our PATH paths. Once run, we’ll be able to call any script in the script folder like it was a system utility.
PATH="$HOME/script_folder/:$PATH"
If you would like to always be able to call any file in your scripts folder, add the above command to your ~/.bashrc file.
You may need to restart your session for it to work.
Issue was not being able to import a video into Peertube using a URL.
Peertube was set up to use youtube-dl which is in /var/www/peertube/storage/bin/youtube-dl. Further investigation showed that Peertube calls it with python.
For example
python youtube-dl video-to-download
Usually Python refers to Python 2 where as Python3 refers to Python 3.
We can create a symlink so that python = python3
sudo ln -s /usr/bin/python3 /usr/bin/python
This way when Peertube runs python, it technically will run it with python3.
Note you will probably run into issues if you do have Python 2 installed and need it. In my case, python was not installed and didn’t reference anything.
While the UniFi controller is nice and everything, it does make it hard to see if a device is already adopted. At least if you have a ton of sites. Fortunately, we can search the database directly to find out if a UniFi is already adopted and which site it is assigned to.
First we need to connect to MongoDB. And then we need to use the ace database.
mongo -port 27117
use ace
This command will list all the devices on the controller. Regardless of which site they are assigned to.
db.device.find({}, { site_id:"", ip : "", name :"", mac:""})
Example output
{ "_id" : ObjectId("563a4d94e4b054e5376fc600"), "mac" : { "_id" : ObjectId("563a4d94e4b054e5376fc600"), "mac" : "44:d9:e7:34:d1:08", "ip" : "192.168.1.200", "name" : "Main_WiFi", "site_id" : "39485e9abf0e9a047bcded96" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("9873b39ed1f5d30a6738abe"), "mac" : "44:d9:e7:01:a3:d4", "ip" : "192.168.1.201", "name" : "Testing_Wifi", "site_id" : "39485e9abf0e9a047bcded96" }
Each UniFi will have a “site_id”. You can use that ID to figure out which site it is assigned to.
db.site.find()
Example output
{ "_id" : ObjectId("39485e9abf0e9a047bcded96"), "name" : "default", "desc" : "Testing Site", "attr_hidden_id" : "default", "attr_no_delete" : true, "anonymous_id" : "83ae20ba-2948-458e-fd0a-1320583ecb04" }
Using our “site_id” from above, we see that the Testing_Wifi device is assigned to the “Testing Site” on the controller.
Something else to look at would be to use the UniFi controller API.
It is sometimes helpful to pull an APK from a working device so you can install it on a different device. These commands should work on an emulator, phone, tablet, or other Android device. You just need to be able to connect with ABD.
This will display a list of all the installed packages.
adb shell pm list packages
Replace com.android.apk with the app of interest.
adb shell pm path com.android.apk
Pull/Download the APK of interest to your local machine with the following command. Change the path “/data/app/…” to the path returned from the previous command.
adb shell pull /data/app/info/base.apk
You can view the following link for more information.
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/4032960/how-do-i-get-an-apk-file-from-an-android-device
What if you need to get an APK off a secondary profile, or would like to download all the APKs off a system? And what about split APKs?
Run the following command to list the users.
adb shell pm list users
Example return
Users:
UserInfo{0:User:a41} running
UserInfo{11:User:439} running
In this case our second user id is 11. To get a list of APKs installed for our second user we would specify the –user= option
adb shell pm list packages --user=11
To get the path for the app we would run it with
adb shell pm path --user=11 com.android.apk
Split APKs can be slightly more difficult to manage, mainly due to the fact that there are multiple APKs to keep track of.
When you run the “pm path” command, it should return multiple APKs. Use the pull command like normal, but download each APK.
You’ll need to use a split APK installer to install all the APKs.
The following PowerShell script will download all APKs for a specific user and put them in their own folders.
This script will pull all the APKs off of a device and put them in the current folder.
It will also download split APKs.
# adbapkbackup uses adb to get a list of all the APKs you have on a phone and then
# Creates folders for each app and downloads the APKs for those apps.
# Copy and save code as a ps1 file
# Enable ps1 scripts to run on your computer by launching an Admin promopt and running
# set-executionpolicy remotesigned
# If you are in a secondary profile, add and/or modify
# "--user 15"
# to your user id
# adb shell pm list users
# If in secondary profile, add "--user 15" after packages before > apklist.txt
adb shell pm list packages --user 15 > apklist.txt
$apks = ((Get-Content .\apklist.txt)) -replace 'package:',''
ForEach ($apk in $apks) {
echo "APK is $apk"
md $apk
# If in secondary profile, add "--user 15" after path, before $file
adb shell pm path $apk
$filepath = ((adb shell pm path --user 15 $apk | % {$_.replace("package:","")}))
ForEach ($lapk in $filepath | % {$_.replace("package:","")}) {
echo "pulling $lapk $apk"
adb pull $lapk $apk
}
}
the “magic bytes” are the first few bytes of a file that can tell you what format the file is.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_file_signatures
Mikrotik Backup file magic bytes
| File type | Magic bytes |
| RC4 Encrypted | EFA89172 |
| AES Encrypted | EFA89173 |
| Not Encrypted | 88ACA1B1 |
Using the above list, we can view a Mikrotik .backup file in a hex editor like GHex or dump it with xxd.
Thanks to the guys who put together the information at the following links.
https://wadman.co.nz/2021/01/02/Viewing-LibreNMS-data-in-Grafana/
https://www.reddit.com/r/LibreNMS/comments/ojc8cc/how_to_almost_natively_integrate_librenms_and/
I ran into some issues trying to get this to work. So here are some of my notes. I already had a LibreNMS installation set up.
NOTE FOR CENTOS 8, ALMALINUX 8 and 9
The steps for installing RRDReST are slightly different. Check out the following post.
https://www.incredigeek.com/home/setting-up-rrdrest-on-centos-8-or-almalinux-9/
I had issues installing RRDReST. I am guessing it had to do with it accessing files. I was able to install it in a docker container.
sudo yum install -y docker docker-compose
sudo systemctl enable docker
Create docker compose file with the following options
vi docker-compose.yml
Change the TZ to your time zone. If you have issues with the graphs, most likely something is off with the time zone between this container and Grafana/LibreNMS server
version: "3.5"
services:
rrdrest:
image: michaelwadman/rrdrest:latest
container_name: rrdrest
restart: always
volumes:
- "/opt/librenms:/opt/librenms"
environment:
- TZ=America/Denver
Save the file and start and setup the container with
sudo docker-compose up -d
You will need your docker container IP address to setup the connection in Grafana
sudo docker exec -it rrdrest ip addr | grep eth0
Congratulations. You should now have a RRDReST docker container that will auto start on system boot and has the correct time zone.
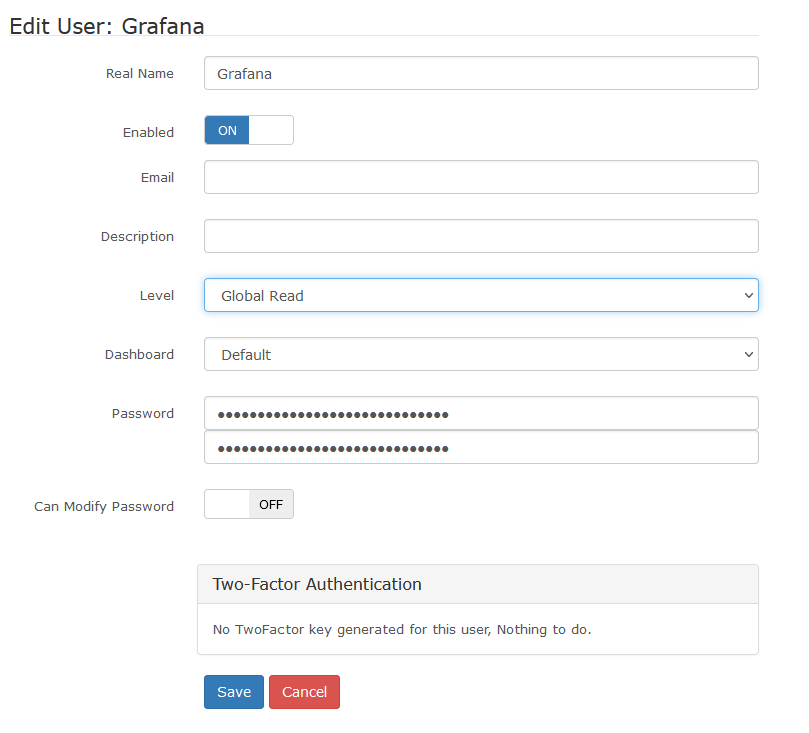
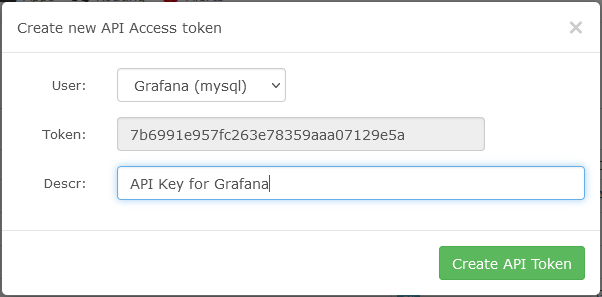
Basic steps are as follows
There is not anything special with installing Grafana on the same server as LibreNMS. You can follow the official guide to install it
https://grafana.com/docs/grafana/latest/installation/
After Grafana is installed, install the JSON API data source. You can do this using the grafana-cli
grafana-cli plugins install marcusolsson-json-datasource
A note on SSL/TLS certificates. If you have an SSL certificate for LibreNMS, you can use it for grafana. If you run into issues, try copying the cert (fullchain.pem, privkey.pem) to /etc/grafana/
You’ll most likely need to change owner
sudo chown root:grafana /etc/grafana/*.pem
And maybe the file permissions.
sudo chmod 640 /etc/grafana/*.pem
This is fairly straight forward.
grafana-cli plugins install marcusolsson-json-datasource
In Grafana, go to Configuration -> Data Sources -> Add data source
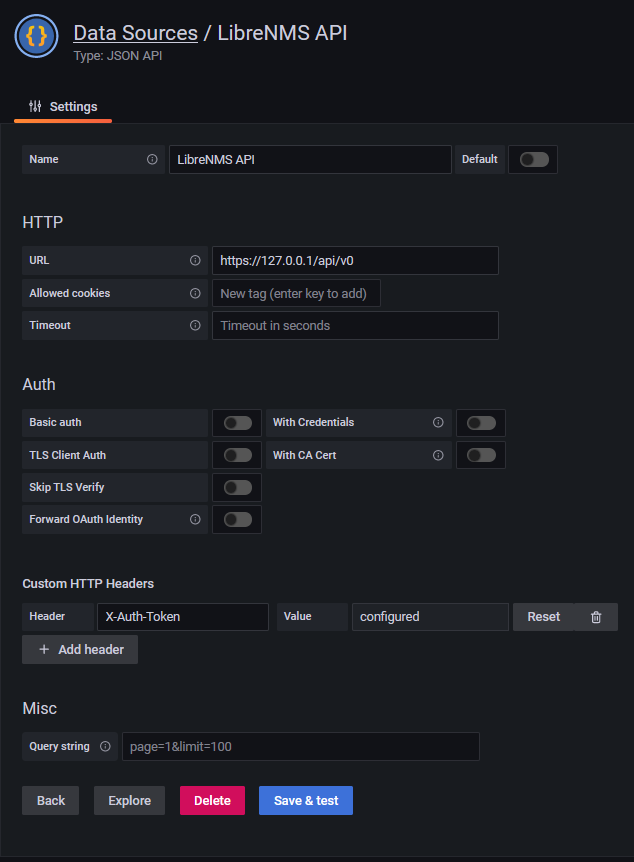
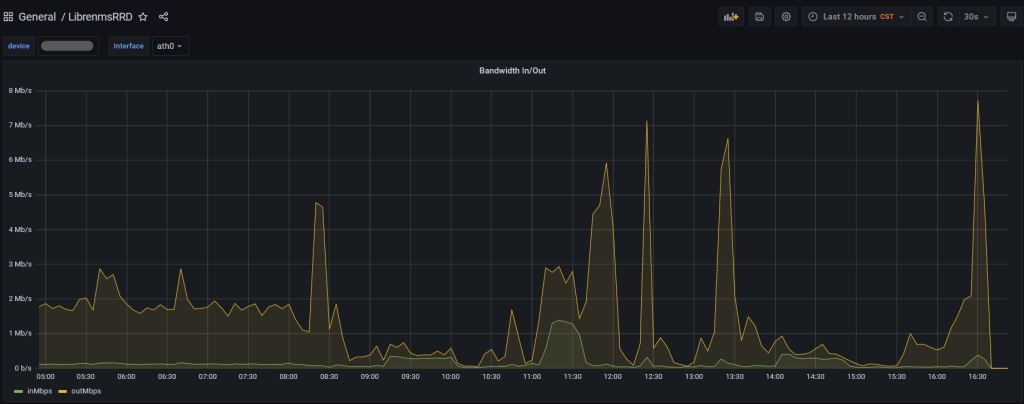
You should now be able to view your dashboard and use the drop down menus to select devices
There were a couple of issues I ran into while trying to get everything working together.
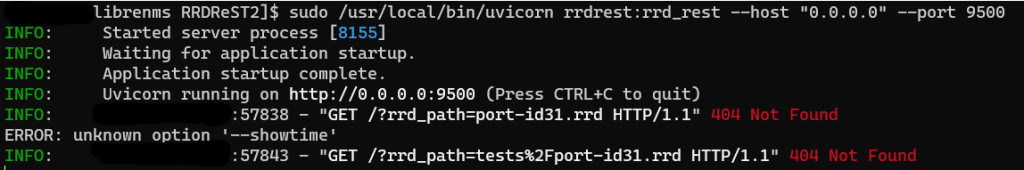
Issue: When trying to run RRDReST with uvicorn, I was never able to access the rrd files, even the test rrd files that are included when installing RRDReST. I am guessing it is either a permisions issue, or something unable to access the files.
Work around: Install RRDReST via Docker container.
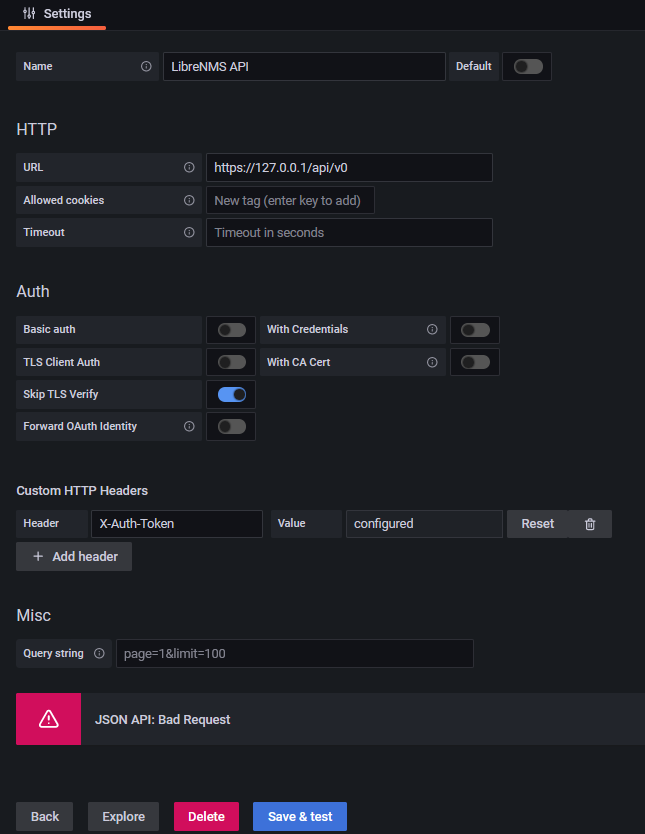
Issue: Get a “JSON API: Bad Request” when trying to set up the LibreNMS API Data Source in Grafana.
Work around: Install a valid SSL Certificate and set up a DNS record so you can access LibreNMS at librenms.yourdomain.com.
More info: I would assume that “Skip TLS Verify” would work with or without a valid certificate, but it would not work for me. There are potentially some other options with modifying how Nginx or Apache is set up that would get this working. If you setup Grafana to use a SSL certificate, you may need to copy the certificate files (fullchain.pem, privkey.pem) to /etc/grafana/ and run “chown root:grafana *.pem” to let grafana have access to the files.
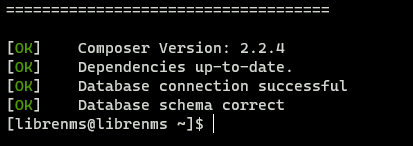
Running the ./validate.php script returns the following error
[FAIL] Python3 module issue found: 'Required packages: ['PyMySQL!=1.0.0', 'python-dotenv', 'redis>=3.0', 'setuptools', 'psutil>=5.6.0', 'command_runner>=1.3.0']
Package not found: The 'command_runner>=1.3.0' distribution was not found and is required by the application
'
[FIX]:
pip3 install -r /opt/librenms/requirements.txt
Running the [FIX] throws an error saying gcc failed with exit status 1.
Fortunately this issue is easy to resolve.
First we need to install python3-devel
sudo yum install python3-devel
Next, as the librenms user, run the pip command to install the requirements.
pip3 install --user -U -r /opt/librenms/requirements.txt
Run ./validate.php to verify that everything is working.